Germany holds the 6th pace, for having the most coal in the world, and yet, it wishes to quit the coal industry within 20 years? Why is it that despite having a large amount coal, Germany still wishes to close down its coal industry?
Summary
- Germany is the 8th largest producer, and the 4th largest consumer in the world
- Germany holds nearly 40 trillion tons of coal
- Germany has spent 44 billion in order to close all coal mines by 2040
- Australia is the 4th largest producer in the world, and exports 4/5 of their production
- The coal industry is expected to decline, as renewables become cheaper to produce and use
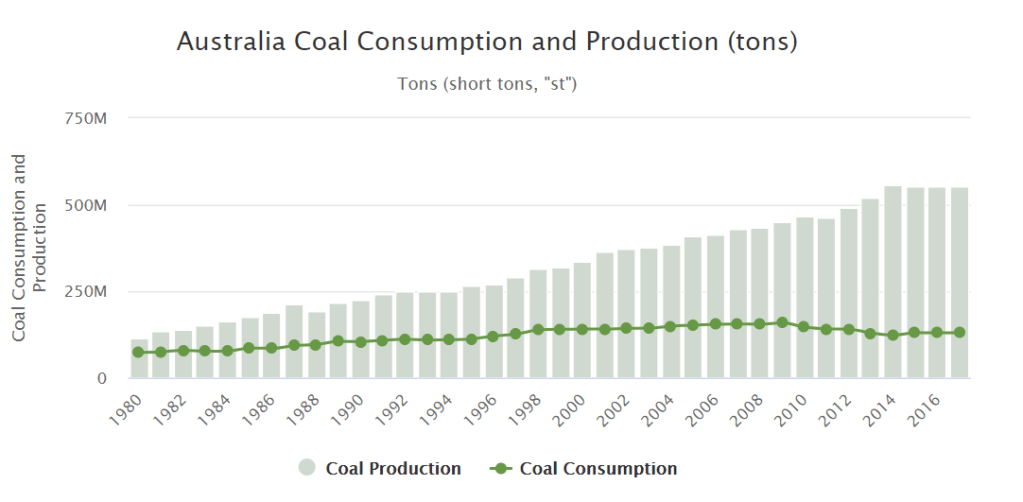
Australia’s coal industry has significantly grown since the 80’s now exporting over 500 million tons of coal each year, bringing Australia a yearly revenue of 5 billion in royalties, and 254 million in payrol taxes, providing around 160,000 jobs across Australia, with the average wage being a cut above 155,000 dolars yearly.
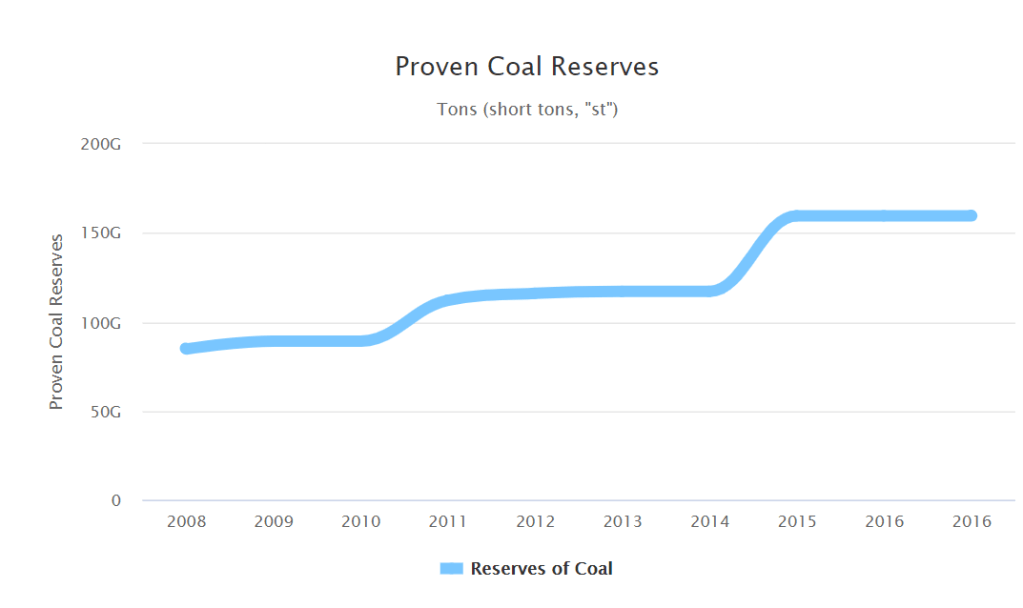
However, not only are our coal reserves not depleting, we are finding even more reserves of coal, with Australia hoping to expand with China’s new project to build even more coal factories. it is expected that with our current rate of mining, Australia will last at least another 1000 years of mining. This shows that our reserve of coal is plentiful, and will not be running out any time soon.
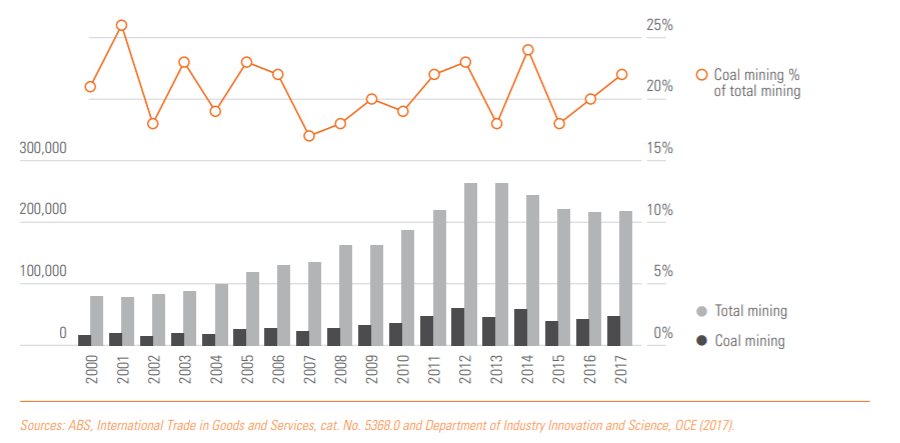
However, the national univeristy has predicted that the coal industry will be a dying industry, with the rise of renewable energy on the rise. In the past 15 years, Coal has had an 80% share in electrical production in the past 15 years, now renewable energy holds around 23% of the electrical production in Australia. since renewable energy is constantly getting cheaper, it is predicted that the coal industry will start declining. As shown in the picture, coal mining has been fluctuating within the past 5 years, and the future is coal is uncertain. Although the coal exports should be stabe within the next 10 years, the national university has predicted coal to start declining after this time period.
References
ABC News. (2020). German coal power plant. [online] Available at: https://www.abc.net.au/news/2020-02-23/german-coal-power-plant/11991384 [Accessed 18 Feb. 2020].
Campbell, E. (2020). Europe’s biggest economy is quitting coal, so far without sacking a single worker. [online] ABC News. Available at: https://www.abc.net.au/news/2020-02-18/australia-climate-how-germany-is-closing-down-its-coal-industry/11902884 [Accessed 20 Feb. 2020].
Jotzo, F., Mazouz, S. and Wiseman, J. et al (2018), Coal transition in Australia: an
overview of issues, CCEP Working Paper 1903, Sep 2018. Crawford School of Public
Policy, The Australian National University.
Minerals Council of Australia. (2020). Coal’s Economic Contribution. [online] Available at: https://minerals.org.au/coal-community [Accessed 20 Feb. 2020].
Sengupta, S. and Eddy, M. (2020). How Hard Is It to Quit Coal? For Germany, 18 Years and $44 Billion. [online] Nytimes.com. Available at: https://www.nytimes.com/2020/01/16/climate/germany-coal-climate-change.html [Accessed 20 Feb. 2020].
Worldometers.info. (2020). Australia Coal Reserves and Consumption Statistics – Worldometer. [online] Available at: https://www.worldometers.info/coal/australia-coal/#coal-reserves [Accessed 23 Feb. 2020].
